Anti-GluN2A/NR2A Antibody (56546)
Anti-GluN2A/NR2A Antibody (56546)
Product No.: 56546
- -
- -
Clone S327-95 Target GluN2A/NR2A Formats AvailableView All Product Type Monoclonal Alternate Names GluN2A, Glutamate [NMDA] receptor subunitε-1, N-methyl D-aspartate receptor subtype 2A, NMDAR2A, NR2A Isotype Mouse IgG2a Applications ICC , IF , IHC , WB |
Data
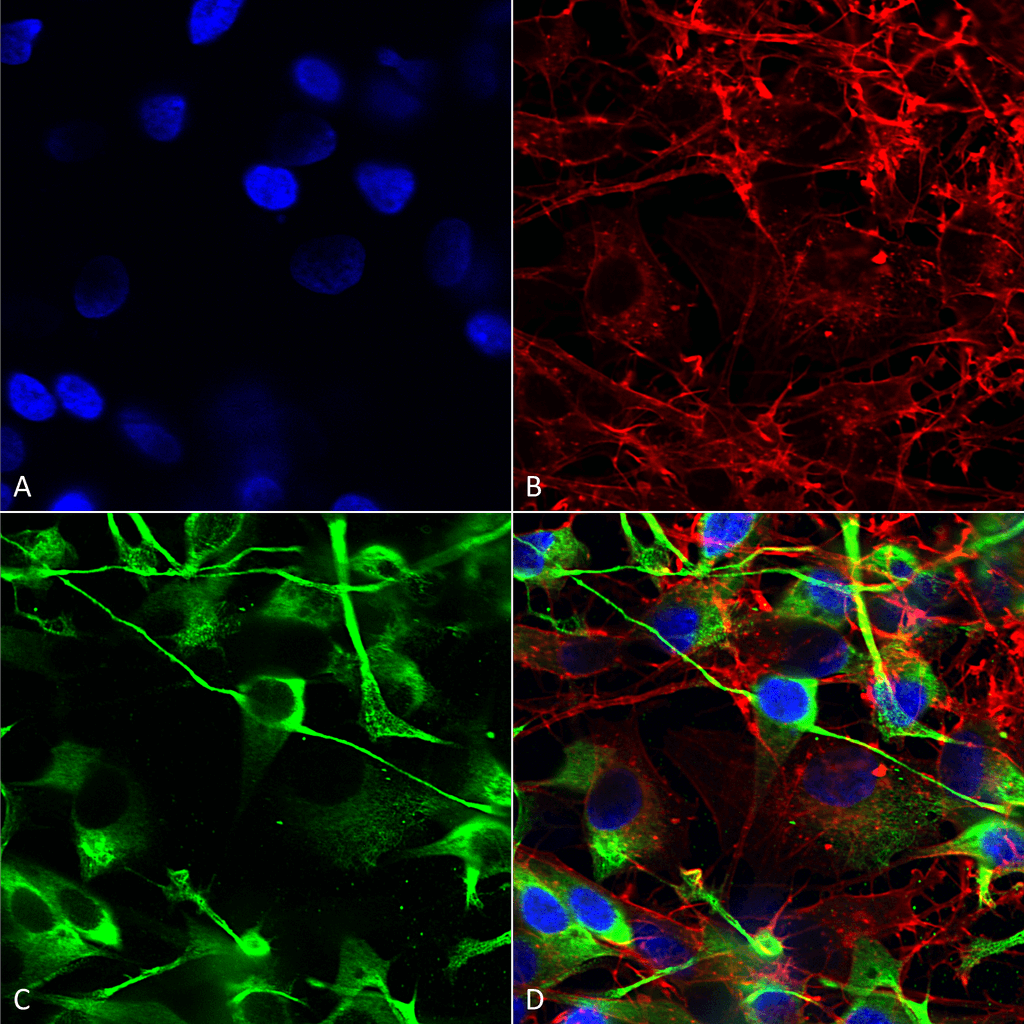 Immunocytochemistry/Immunofluorescence analysis using Mouse Anti-GluN2A/NR2A Monoclonal Antibody, Clone S327-95 (56546). Tissue: Neuroblastoma cells (SH-SY5Y). Species: Human. Fixation: 4% PFA for 15 min. Primary Antibody: Mouse Anti-GluN2A/NR2A Monoclonal Antibody (56546) at 1:200 for overnight at 4°C with slow rocking. Secondary Antibody: AlexaFluor 488 at 1:1000 for 1 hour at RT. Counterstain: Phalloidin-iFluor 647 (red) F-Actin stain; Hoechst (blue) nuclear stain at 1:800, 1.6mM for 20 min at RT. (A) Hoechst (blue) nuclear stain. (B) Phalloidin-iFluor 647 (red) F-Actin stain. (C) GluN2A/NR2A Antibody (D) Composite.
Immunocytochemistry/Immunofluorescence analysis using Mouse Anti-GluN2A/NR2A Monoclonal Antibody, Clone S327-95 (56546). Tissue: Neuroblastoma cells (SH-SY5Y). Species: Human. Fixation: 4% PFA for 15 min. Primary Antibody: Mouse Anti-GluN2A/NR2A Monoclonal Antibody (56546) at 1:200 for overnight at 4°C with slow rocking. Secondary Antibody: AlexaFluor 488 at 1:1000 for 1 hour at RT. Counterstain: Phalloidin-iFluor 647 (red) F-Actin stain; Hoechst (blue) nuclear stain at 1:800, 1.6mM for 20 min at RT. (A) Hoechst (blue) nuclear stain. (B) Phalloidin-iFluor 647 (red) F-Actin stain. (C) GluN2A/NR2A Antibody (D) Composite.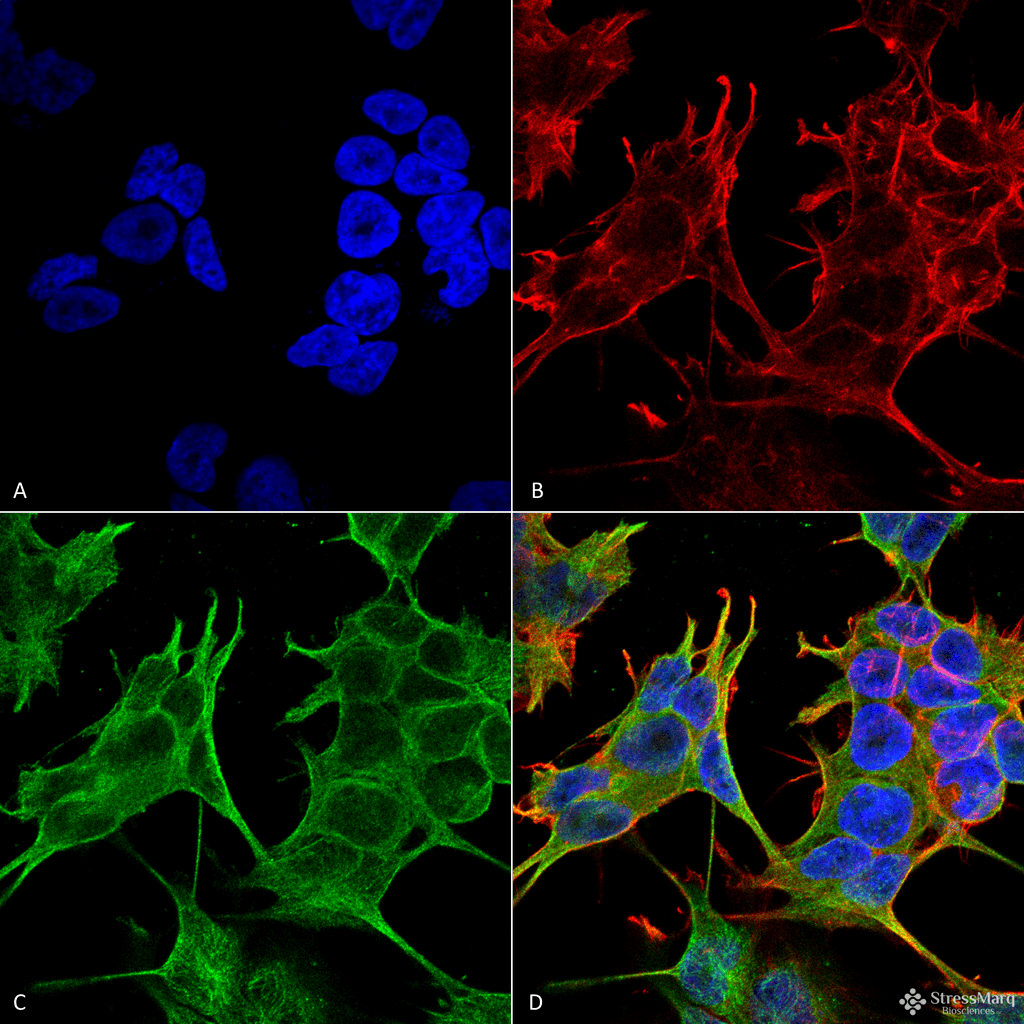 Immunocytochemistry/Immunofluorescence analysis using Mouse Anti-GluN2A/NR2A Monoclonal Antibody, Clone S327-95 (56546). Tissue: Neuroblastoma cell line (SK-N-BE). Species: Human. Fixation: 4% Formaldehyde for 15 min at RT. Primary Antibody: Mouse Anti-GluN2A/NR2A Monoclonal Antibody (56546) at 1:100 for 60 min at RT. Secondary Antibody: Goat Anti-Mouse ATTO 488 at 1:100 for 60 min at RT. Counterstain: Phalloidin Texas Red F-Actin stain; DAPI (blue) nuclear stain at 1:1000, 1:5000 for 60min RT, 5min RT. Localization: Cell Membrane, Cell Junction. Magnification: 60X. (A) DAPI (blue) nuclear stain. (B) Phalloidin Texas Red F-Actin stain. (C) GluN2A/NR2A Antibody. (D) Composite.
Immunocytochemistry/Immunofluorescence analysis using Mouse Anti-GluN2A/NR2A Monoclonal Antibody, Clone S327-95 (56546). Tissue: Neuroblastoma cell line (SK-N-BE). Species: Human. Fixation: 4% Formaldehyde for 15 min at RT. Primary Antibody: Mouse Anti-GluN2A/NR2A Monoclonal Antibody (56546) at 1:100 for 60 min at RT. Secondary Antibody: Goat Anti-Mouse ATTO 488 at 1:100 for 60 min at RT. Counterstain: Phalloidin Texas Red F-Actin stain; DAPI (blue) nuclear stain at 1:1000, 1:5000 for 60min RT, 5min RT. Localization: Cell Membrane, Cell Junction. Magnification: 60X. (A) DAPI (blue) nuclear stain. (B) Phalloidin Texas Red F-Actin stain. (C) GluN2A/NR2A Antibody. (D) Composite.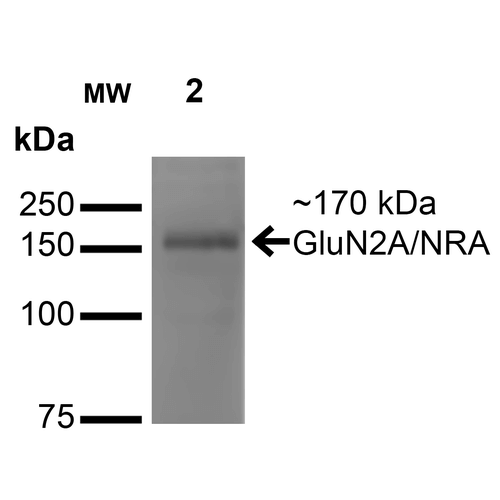 Western Blot analysis of Monkey COS cells transfected with GFP-tagged NR2A showing detection of ~170 kDa GluN2A/NR2A protein using Mouse Anti-GluN2A/NR2A Monoclonal Antibody, Clone S327-95 (56546). Lane 1: Molecular Weight Ladder. Lane 2: Monkey COS cells transfected with GFP-tagged NR2A. Load: 15 µg. Block: 2% BSA and 2% Skim Milk in 1X TBST. Primary Antibody: Mouse Anti-GluN2A/NR2A Monoclonal Antibody (56546) at 1:200 for 16 hours at 4°C. Secondary Antibody: Goat Anti-Mouse IgG: HRP at 1:1000 for 1 hour RT. Color Development: ECL solution for 6 min in RT. Predicted/Observed Size: ~170 kDa. Other Band(s): 100 kDa.
Western Blot analysis of Monkey COS cells transfected with GFP-tagged NR2A showing detection of ~170 kDa GluN2A/NR2A protein using Mouse Anti-GluN2A/NR2A Monoclonal Antibody, Clone S327-95 (56546). Lane 1: Molecular Weight Ladder. Lane 2: Monkey COS cells transfected with GFP-tagged NR2A. Load: 15 µg. Block: 2% BSA and 2% Skim Milk in 1X TBST. Primary Antibody: Mouse Anti-GluN2A/NR2A Monoclonal Antibody (56546) at 1:200 for 16 hours at 4°C. Secondary Antibody: Goat Anti-Mouse IgG: HRP at 1:1000 for 1 hour RT. Color Development: ECL solution for 6 min in RT. Predicted/Observed Size: ~170 kDa. Other Band(s): 100 kDa. - -
- -
Antibody DetailsProduct DetailsReactive Species Human ⋅ Mouse ⋅ Rat Host Species Mouse Immunogen Fusion protein corresponding to aa 75-325 (extracellular N-terminus) of rat GluN2A/NR2A (accession no. Q00959). Product Concentration Lot Specific Formulation PBS, pH 7.4; 50% glycerol, 0.09% sodium azide. State of Matter Liquid Product Preparation Purified by Protein G affinity chromatography Storage and Handling This antibody is stable for at least one (1) year at -20°C. Avoid repeated freezing
and thawing. Regulatory Status For in vitro investigational use only. Not for
use in therapeutic or diagnostic procedures. Country of Origin USA Shipping Next Day 2-8°C Applications and Recommended Usage? Quality Tested by Leinco Immunoblotting: use at 1ug/mL. A band of ~170kDa is detected.
Positive control: Rat brain lysate. These are recommended concentrations. User should determine optimal concentrations for their application. Each investigator should determine their own optimal working dilution for specific applications. See directions on lot specific datasheets, as information may periodically change. DescriptionDescriptionSpecificity This antibody recognizes human, mouse,
and rat GluN2A/NR2A. It does not cross-react with NR2B. Background N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors are heteromeric protein complexes, and three families of NMDAR subunits have been identified: NR1, NR2 and NR3. The subunit composition determines the pharmacological and physiological properties of the NMDARs. NR2A is gradually increased in adult CNS but is absent in embryonic CNS. Electro- physiological data suggest that NR2A- containing NMDARs tend to be localized synaptically, whereas NR2B-containing receptors tend to be localized peri- synaptically or extrasynaptically. In the spinal cord, the predominant subunits of NMDARs include NR2A at synaptic sites and NR2B at extrasynaptic sites. Function Component of NMDA receptor complexes that function as heterotetrameric, ligand-gated ion channels with high calcium permeability and voltage-dependent sensitivity to magnesium. Channel activation requires binding of the neurotransmitter glutamate to the epsilon subunit, glycine binding to the zeta subunit, plus membrane depolarization to eliminate channel inhibition by Mg(2+). Sensitivity to glutamate and channel kinetics depend on the subunit composition; channels containing GRIN1 and GRIN2A have lower sensitivity to glutamate and faster deactivation kinetics than channels formed by GRIN1 and GRIN2B (PubMed:28384476). Contributes to the slow phase of excitatory postsynaptic current, long-term synaptic potentiation, and learning (By similarity). {UniProtKB:P35436, PubMed:1350383, PubMed:16281028, PubMed:23625947, PubMed:24462099, PubMed:26679993, PubMed:27618671, PubMed:27916457, PubMed:28384476, PubMed:28468946, PubMed:28760974, PubMed:8428958}. NCBI Gene Bank ID UniProt.org Research Area Neuroscience References & CitationsTechnical ProtocolsCertificate of Analysis |


