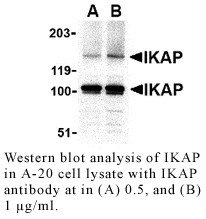
Anti-Human IKK Complex-Associated Protein (IKAP)
Data
- -
- -
Antibody DetailsProduct DetailsReactive Species Human Host Species Rabbit Immunogen PN:I-475 Formulation This polyclonal antibody is formulated in phosphate buffered saline (PBS) pH 7.4 containing 0.02% sodium azide as a preservative. Storage and Handling This polyclonal antibody is stable for at least one week when stored at 2-8°C. For long term storage, aliquot in working volumes without diluting and store at –20°C in a manual defrost freezer. Avoid Repeated Freeze Thaw Cycles. Country of Origin USA Shipping Next Day Ambient RRIDAB_2830697 Each investigator should determine their own optimal working dilution for specific applications. See directions on lot specific datasheets, as information may periodically change. DescriptionDescriptionSpecificity Rabbit Anti-Human IKK Complex-Associated Protein (IKAP) recognizes Human and Mouse IKAP. This polyclonal antibody was purified using affinity chromatography. Background IKAP was initially identified as a scaffold protein of the IκB kinase complex that could bind to IKKα, IKKβ, NF-κB, and the NF-κB-inducing kinase (NIK), although later evidence has cast doubt on this. More recent reports show that mutations in IKAP such as a frameshift leading to a truncated protein or a missense mutation that leads to defective phosphorylation are responsible for the autosomal recessive genetic disease familial dysautonomia (FD). Reports indicating that it forms part of the RNA polymerase II transcription elongation complex suggest that this disease may be due to compromised transcription elongation. More recently, it was shown that IKAP associates with c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) and could specifically enhance JNK activation induced by the upstream JNK activators MEKK1 and ASK1, indicating another possible cause for FD. At least two isoforms of IKAP are known two exist. PubMed References & Citations1. Cohen, L. et al. (1998) Nature 395:292 2. Krappmann, D. et al. (2000) J. Biol. Chem. 275:29779 3. Anderson, S L. et al. (2001) Am. J. Hum. Genet.68:753 4. Hawkes, N. A. et al. (2002) J. Biol. Chem. 277:3047 Technical ProtocolsCertificate of Analysis |
Related Products
 Products are for research use only. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.
Products are for research use only. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.