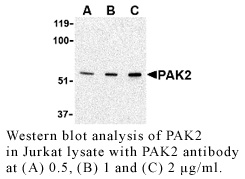
Anti-Human P21-Activated Kinase 2 (NT) (PAK2)
Data
- -
- -
Antibody DetailsProduct DetailsReactive Species Human Host Species Rabbit Immunogen PN:P199 Product Concentration 0.5 mg/ml Formulation This polyclonal antibody is formulated in phosphate buffered saline (PBS) pH 7.4 containing 0.02% sodium azide as a preservative. Storage and Handling This polyclonal antibody is stable for at least one week when stored at 2-8°C. For long term storage, aliquot in working volumes without diluting and store at –20°C in a manual defrost freezer. Avoid Repeated Freeze Thaw Cycles. Country of Origin USA Shipping Next Day Ambient RRIDAB_2831538 Each investigator should determine their own optimal working dilution for specific applications. See directions on lot specific datasheets, as information may periodically change. DescriptionDescriptionSpecificity Rabbit Anti-Human P21-Activated Kinase 2 (PAK2) recognizes an epitope near the N-terminus of Human, Mouse and Rat PAK2. This polyclonal antibody was purified using affinity chromatography. Background The p21-activated kinases (PAKs) are serine-threonine kinases that bind to the active forms of Cdc42 and Rac. They are divided into two groups, the first of which include PAK1, 2 and 3, and can be activated by Cdc42/Rac binding. Group 1 PAKs contain an autoinhibitory domain whose activity is regulated by Cdc42/Rac binding. The group 1 PAKs are known to be involved in cellular processes such as gene transcription, apoptosis, and cell morphology and motility. Much less is known about the second group, which includes PAK4, 5 and 6, and are not activated by Cdc42/Rac binding. Of the six PAK proteins, only PAK2 is ubiquitously expressed and cleaved by caspase-3. This cleavage removes the amino-terminal regulatory domain and generates a constitutively active kinase fragment. Recent experiments have shown that following cleavage, the active fragment is myristoylated and directed to the plasma membrane and membrane ruffles where it promotes cell death via increased signaling through the c-Jun N-terminal kinase pathway, but without compromising mitochondrial integrity. PubMed References & Citations1. Jaffer, ZM. et al. (2004) Cell Biol. 34:713 2. Rudel, T. et al. (1997) Science 276:1571 3. Vilas, GL. et al. (2006) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 103:6542 Technical ProtocolsCertificate of Analysis |
Related Products
- -
- -