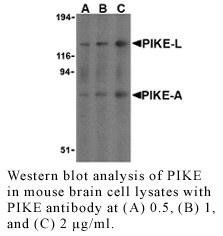
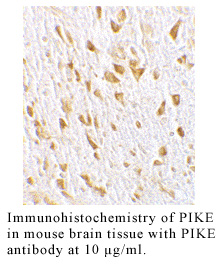
Anti-Human PIKE (CT)
Data
- -
- -
Antibody DetailsProduct DetailsReactive Species Human Host Species Rabbit Immunogen PN:P222 Product Concentration 0.5 mg/ml Formulation This polyclonal antibody is formulated in phosphate buffered saline (PBS) pH 7.4 containing 0.02% sodium azide as a preservative. Storage and Handling This polyclonal antibody is stable for at least one week when stored at 2-8°C. For long term storage, aliquot in working volumes without diluting and store at –20°C in a manual defrost freezer. Avoid Repeated Freeze Thaw Cycles. Country of Origin USA Shipping Next Day Ambient RRIDAB_2831551 Each investigator should determine their own optimal working dilution for specific applications. See directions on lot specific datasheets, as information may periodically change. DescriptionDescriptionSpecificity Rabbit Anti-Human PIKE recognizes an epitope near the C-terminus of Human and Mouse PIKE. This polyclonal antibody was purified using affinity chromatography. Background Phosphoinositide 3 kinase enhancer (PIKE) is a recently identified nuclear GTPase that interacts with nuclear phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3 kinase) to stimulate its lipid kinase activity (1). PIKE exists in multiple isoforms; a shorter C-terminal isoform (PIKE-A) has also been identified as centaurin γ 1 (reviewed in 2). The longest isoform (PIKE-L) has been shown to bind to the adaptor protein Homer and thereby link to metabotropic glutamate receptors, leading to activation of PI3 kinase activity and prevention of neuronal apoptosis.3 Overexpression of PIKE-A enhances Akt activity and promotes cancer cell invasion, whereas decreased expression of PIKE-A via dominant negative expression of PIKE-A or PIKE-A knockdown inhibits these processes.4 In many human cancers, expression of PIKE-A is enhanced, leading to increased Akt activity and preventing apoptosis. PubMed References & Citations1. Ye, K. et al. (2000) Cell 103:919 2. Jackson, TR. et al. (2000) Trends Biochem. Sci. 25:489 3. Rong, R. et al. (2003) Nat. Neurosci. 6:1153 4. Ahn, JY. et al. (2004) J. Biol. Chem. 279:16441 Technical ProtocolsCertificate of Analysis |