Anti-Human PSAP Antibody (34070)
Anti-Human PSAP Antibody (34070)
Product No.: 34070
- -
- -
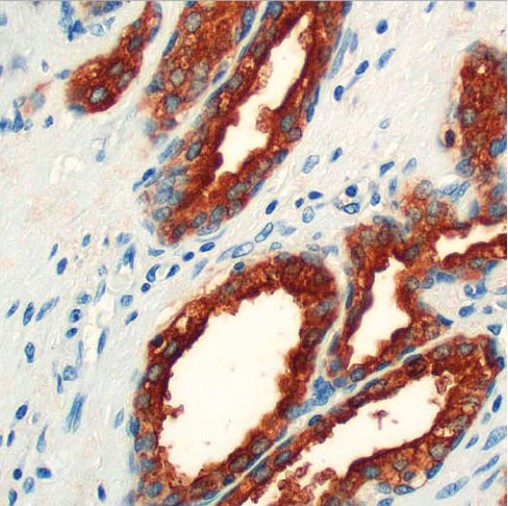
Clone G655.1 Target PSAP Formats AvailableView All Product Type Monoclonal Alternate Names Proactivator polypeptide [Cleaved into: Saposin-A Isotype Mouse IgG1 Applications IHC |
Data
- -
- -
Antibody DetailsProduct DetailsReactive Species Human Host Species Mouse Immunogen Recombinant human PSAP. Formulation Tris buffer, pH 7.3-7.7, 1% BSA, State of Matter Liquid Product Preparation Purified by immunoaffinity chromatography Storage and Handling Store at 2-8°C. Do not freeze. Shipping Next Day 2-8°C Applications and Recommended Usage? Quality Tested by Leinco Immunohistochemistry: use at a dilution of 1:100-1:200 on formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded samples after heat-induced epitope retrieval at pH 9 for 10-30 minutes. Each investigator should determine their own optimal working dilution for specific applications. See directions on lot specific datasheets, as information may periodically change. DescriptionDescriptionSpecificity Mouse Monoclonal Antibody specific to PSAP Background Prostatic Specific Acid Phosphatase (PSAP) is an enzyme found in the glandular epithelium of the prostate. PSAP levels are elevated in hyperplastic prostate and prostate carcinoma with the highest levels being detected in metastasized prostate cancer. Moderate overexpression of PSAP is also characteristic of diseases of the bone (such as Paget's disease or hyperparathyroidism), diseases of blood cells (such as sickle-cell disease), multiple myeloma, or lysosomal storage diseases such as Gaucher's disease. Function Saposin-A and saposin-C stimulate the hydrolysis of glucosylceramide by beta-glucosylceramidase (EC 3.2.1.45) and galactosylceramide by beta-galactosylceramidase (EC 3.2.1.46). Saposin-C apparently acts by combining with the enzyme and acidic lipid to form an activated complex, rather than by solubilizing the substrate.; Saposin-B stimulates the hydrolysis of galacto-cerebroside sulfate by arylsulfatase A (EC 3.1.6.8), GM1 gangliosides by beta-galactosidase (EC 3.2.1.23) and globotriaosylceramide by alpha-galactosidase A (EC 3.2.1.22). Saposin-B forms a solubilizing complex with the substrates of the sphingolipid hydrolases.; Saposin-D is a specific sphingomyelin phosphodiesterase activator (EC 3.1.4.12).; [Prosaposin]: Behaves as a myelinotrophic and neurotrophic factor, these effects are mediated by its G-protein-coupled receptors, GPR37 and GPR37L1, undergoing ligand-mediated internalization followed by ERK phosphorylation signaling. {UniProtKB:Q61207, PubMed:10383054}.; Saposins are specific low-molecular mass non-enzymic proteins, they participate in the lysosomal degradation of sphingolipids, which takes place by the sequential action of specific hydrolases. NCBI Gene Bank ID UniProt.org Research Area Cancer Research References & Citations |