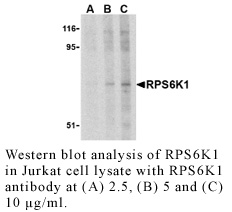
Anti-Human Ribosomal Protein S6 Kinase 1 (RPS6K1)
Data
- -
- -
Antibody DetailsProduct DetailsReactive Species Human Host Species Rabbit Immunogen PN:R1240 Product Concentration 0.5 mg/ml Formulation This polyclonal antibody is formulated in phosphate buffered saline (PBS) pH 7.4 containing 0.02% sodium azide as a preservative. Storage and Handling This polyclonal antibody is stable for at least one week when stored at 2-8°C. For long term storage, aliquot in working volumes without diluting and store at –20°C in a manual defrost freezer. Avoid Repeated Freeze Thaw Cycles. Country of Origin USA Shipping Next Day Ambient RRIDAB_2831685 Each investigator should determine their own optimal working dilution for specific applications. See directions on lot specific datasheets, as information may periodically change. DescriptionDescriptionSpecificity Rabbit Anti-Human Ribosomal Protein S6 Kinase 1 (RPS6K1) recognizes Human RPS6K1. This polyclonal antibody was purified using affinity chromatography. Background Ribosomal protein S6 kinase 1 (RPS6K1) is the best characterized effector of the mammalian Target of Rapamycin (TOR), an evolutionarily conserved serine/threonine kinase that regulates cell growth and cell cycle through its ability to integrate signals from nutrient levels and growth factors/1,2 Nutrients and growth factors stimulate a complex including TOR, raptor (regulatory associated protein of TOR), and GBL to phosphorylate RPS6K1 and the eukaryotic initiation factor 4E binding protein (4EBP1), leading to increased protein synthesis and cell growth.3 RPS6K1 is thought to desensitize tissues to insulin as mice deficient in RPS6K1 have been shown to be hypersensitive to insulin and impervious to obesity-induced insulin resistance seen in wild type obese mice.4 PubMed References & Citations1. Burnett, PE. et al. (1998) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 95:1432 2. Inoki, K. et al. (2005) Mol. Biol. Rev. 69:79 3. Manning, BD. (2004) J. Cell Biol. 167:399 4. Um, SH. et al. (2004) Nature 431:200 Technical ProtocolsCertificate of Analysis |
Related Products
- -
- -