Anti-Mouse IFNAR-1 (Clone MAR1-5A3) – Purified in vivo GOLD™ Functional Grade
Anti-Mouse IFNAR-1 (Clone MAR1-5A3) – Purified in vivo GOLD™ Functional Grade
Product No.: I-401
- -
- -
Clone MAR1-5A3 Target IFNAR1 Formats AvailableView All Product Type Monoclonal Antibody Alternate Names CD118, Ifar, Ifnar, Ifrc, INF-a receptor, Interferon-α/β receptor α chain precursor Isotype Mouse IgG1 Applications B , ELISA , FC , in vivo , IP , WB |
Data
- -
- -
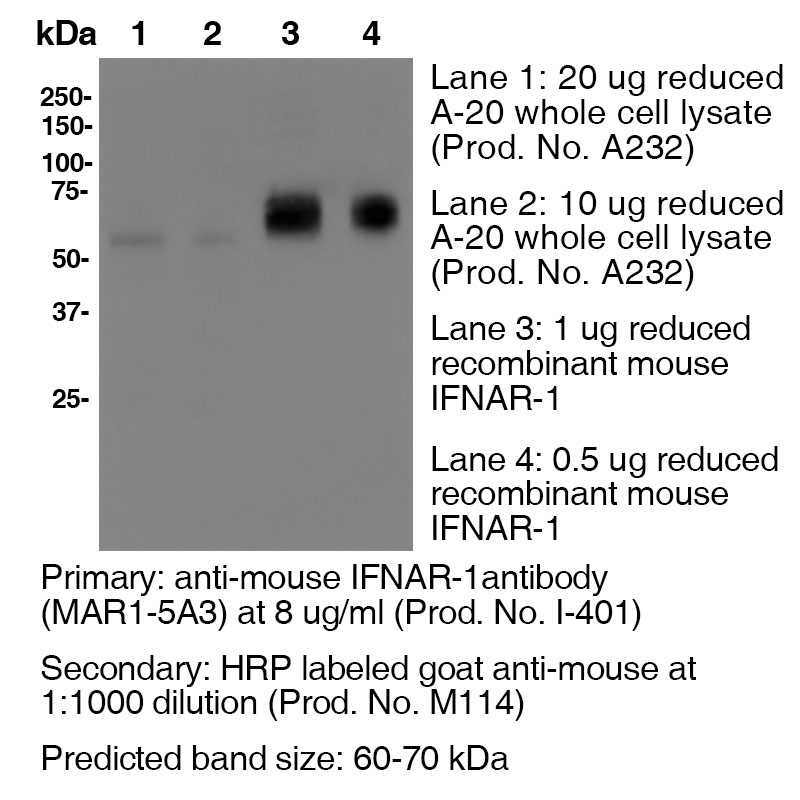
Antibody DetailsProduct DetailsReactive Species Mouse Host Species Mouse Recommended Isotype Controls Recommended Dilution Buffer Immunogen This antibody was produced by In vivo genetic immunization of IFNAR1 knockout mice with a plasmid encoding the extracellular domain of murine IFNAR1. Product Concentration ≥ 5.0 mg/ml Endotoxin Level < 1.0 EU/mg as determined by the LAL method Purity ≥95% monomer by analytical SEC ⋅ >95% by SDS Page Formulation This monoclonal antibody is aseptically packaged and formulated in 0.01 M phosphate buffered saline (150 mM NaCl) PBS pH 7.2 - 7.4 with no carrier protein, potassium, calcium or preservatives added. Due to inherent biochemical properties of antibodies, certain products may be prone to precipitation over time. Precipitation may be removed by aseptic centrifugation and/or filtration. Product Preparation Functional grade preclinical antibodies are manufactured in an animal free facility using in vitro cell culture techniques and are purified by a multi-step process including the use of protein A or G to assure extremely low levels of endotoxins, leachable protein A or aggregates. Storage and Handling Functional grade preclinical antibodies may be stored sterile as received at 2-8°C for up to one month. For longer term storage, aseptically aliquot in working volumes without diluting and store at ≤ -70°C. Avoid Repeated Freeze Thaw Cycles. Country of Origin USA Shipping Next Day 2-8°C RRIDAB_2491621 Applications and Recommended Usage? Quality Tested by Leinco FC The suggested concentration for clone MAR1-5A3 antibody for staining cells in flow cytometry is ≤ 2.0 μg per 106 cells in a volume of 100 μl or 100μl of whole blood. Titration of the reagent is recommended for optimal performance for each application. NOTE: Leinco Technologies suggests using Anti-Mouse IFNAR1-Biotin (With Streptavidin - PE; Part No. S211) (Leinco Product No.: I-402) for flow cytometry of mouse cells Additional Applications Reported In Literature ? B Clone MAR1-5A3 has a short half-life due to the rapid recycling of cells that express the IFNAR1 receptor. In order to block function In vivo, continual blocking of all compartments is necessary. Therefore, a large loading dose is necessary to saturate all In vivo binding sites and should be maintained to ensure binding site saturation. For In vivo blocking studies, a loading dose of 2.5 mg/mouse, followed by a weekly dose of 0.5 mg/mouse is recommended. The half-life following a 2.5 mg loading dose is approximately 5 days. However, if you fail to saturate the binding sites by injecting a low dose of 250 μg, for example, the half life is only 1.5 days. WB For Western blotting, the suggested use of this reagent is 1.0 µg per ml (See Data Results) IP ELISA Each investigator should determine their own optimal working dilution for specific applications. See directions on lot specific datasheets, as information may periodically change. DescriptionDescriptionSpecificity Clone MAR1-5A3 recognizes an epitope on mouse IFNAR1. Background IFNAR1 is a type I membrane protein, that in conjunction with IFNAR2, makes up the heterodimeric receptor that binds all type I IFNs, which includes IFN α and β. Binding and activation of the receptor stimulates Janus protein kinases, which leads to the phosphorylation of several other proteins, namely STAT1 and STAT2. IFNAR1 has also been shown to interact with PRMT1 and Tyrosine kinase 2. Type I IFNs are a family of cytokines that have been shown to promote anti-viral, anti-microbial, anti-tumor and autoimmune responses In vivo. Antigen Distribution IFNAR1 and IFNAR2 are coexpressed on nearly all cells. Ligand/Receptor IFN-α/β PubMed NCBI Gene Bank ID UniProt.org References & Citations1.) Beaver, Jacob T. et al. (2020) Human Vaccines & Immunotherapeutics 16:9, 2092-2108 Article Link 2.) Theofilopoulos, AN. et al. (2012) J Immunol. 189: 000–000. Article Link 3.) Oldstone, Michael B. A. et al. (2017) Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 114(14): 3708–3713. PubMed 4.) Schreiber, RD et al. (2015) PLoS One.10(5):e0128636PubMed 5.) Shin, Haina et al. (2018) J Virol. 92(7): e00038-18. PubMed 6.) Crack, Peter J. et al. (2016) eNeuro 10.1523/ENEURO.0128-15.2016 Article Link 7.) Sheehan, K. C. F. et al. (2006) JICR 26(11):804 8.) Dunn, G. P. et al. (2005) Nat. Immunol. 6(7):722 9.) Fenner, J. E. et al. (2006) Nat. Immunol. 7(1):33 10). Biron, C. A. et al. (2007) J Exp Med. 204(10): 2383 11.) Raju, S et al. (2019) Cell Reports. 29(9):2556–2564.e3 Journal Link 12.) Ortiz, A. et al. (2019) Cancer Cell 35(1):33-45.e6 Journal Link 13.) Case, J. et al. (2020) Cell Host & Microbe. 28(3):465–474.e4 Journal Link 14.) Hassan, A. et al. (2020) Cell. 183(1):169–184.e13 Journal Link 15.) Hassan, A. et al. (2020) Cell. 182(3):744–753.e4 Journal Link 16.) Hassan, A. et al. (2020) Cell. 182(3):901-918.e18 Journal Link 17.) Stine, R. et al. (2019) Cell Stem Cell. 25(6):830–845.e8 Journal Link 18.) White, J. et al. (2018) Cell 175(5):1198-1212.e12 Journal Link 19.) Jagger et al. (2017) Cell Host & Microbe. 22:366–376 Journal Link 20.) Richner, J. et al. (2017) Cell 170(2):273-283.e12 Journal Link 21.) Richner, J. et al. (2017) Cell 168(6):1114-1125.e10 Journal Link 22.) Best, S. et al. (2021) Cell Reports 37(4):109888 Journal Link 23.) Diamond, M. et al. (2021) Cell 184(17):Pages 4414-4429.e19 Journal Link 24.) Ahmed, H.et al. (2021) Cell Reports 36(4): 109452 Journal Link 25.) Lebratti, T.et al. (2021) eLife 10: e65762 Journal Link 26.) Gambino Jr., F.et al. (2021) Cell Reports 35(6): 109107 Journal Link 27.) Earnest, J. et al. (2021) Cell Reports 35(1): 108962 Journal Link 28.) Desai, P. et al. (2021) Cell 184(5):1214-1231.e16 Journal Link 29.) Jagger, B. et al. (2017) Cell Host Microbe 22(3):366-376.e3 Journal Link 30.) VanBlargan, L. et al. (2018) Cell Reports 25(12):10.1016 Journal Link 31.) Lim, J. et al. (2019) eLife 8(e44452):10.7554 Journal Link Technical ProtocolsCertificate of Analysis |
Related Products
- -
- -
Formats Available
- -
- -
Prod No. | Description |
|---|---|
I-400 | |
I-1014 | |
I-1018 | |
I-402 | |
I-401 | |
I-1033 | |
I-1032 | |
I-1188 |