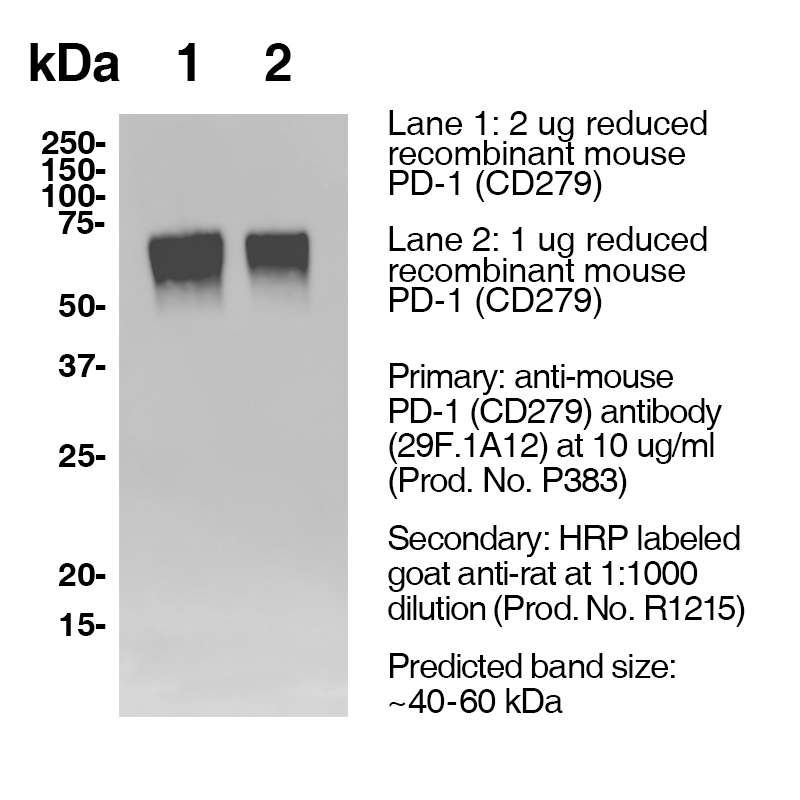
Anti-Mouse CD279 (PD-1) (Clone 29F.1A12) – Purified
Anti-Mouse CD279 (PD-1) (Clone 29F.1A12) – Purified
Product No.: P383
- -
- -
Clone 29F.1A12 Target PD-1 Formats AvailableView All Product Type Monoclonal Antibody Alternate Names Programmed Death-1, CD279 Isotype Rat IgG2a κ Applications FC , IHC FF , PhenoCycler® , WB |
Data
- -
- -
Antibody DetailsProduct DetailsReactive Species Mouse Host Species Rat Immunogen PD-1 cDNA followed by PD-1-Ig fusion protein Product Concentration 0.5 mg/ml Formulation This purified antibody is formulated in 0.01 M phosphate buffered saline (150 mM NaCl) PBS pH 7.4, 1% BSA and 0.09% sodium azide as a preservative. Storage and Handling This purified antibody is stable when stored at 2-8°C. Do not freeze. Country of Origin USA Shipping Next Day 2-8°C RRIDAB_2831656 Each investigator should determine their own optimal working dilution for specific applications. See directions on lot specific datasheets, as information may periodically change. DescriptionDescriptionSpecificity Clone 29F.1A12 recognizes an epitope on mouse PD-1. Background PD-1 is a 50-55 kD member of the B7 Ig superfamily. PD-1 is also a member of the extended CD28/CTLA-4 family of T cell regulators and is suspected to play a role in lymphocyte clonal selection and peripheral tolerance. The ligands of PD-1 are PD-L1 and PD-L2, and are also members of the B7 Ig superfamily. PD-1 and its ligands negatively regulate immune responses. PD-L1, or B7-Homolog 1, is a 40 kD type I transmembrane protein that has been reported to costimulate T cell growth and cytokine production. The interaction of PD-1 with its ligand PD-L1 is critical in the inhibition of T cell responses that include T cell proliferation and cytokine production. PD-L1 has increased expression in several cancers. Inhibition of the interaction between PD-1 and PD-L1 can serve as an immune checkpoint blockade by improving T-cell responses In vitro and mediating preclinical antitumor activity. Within the field of checkpoint inhibition, combination therapy using anti-PD1 in conjunction with anti-CTLA4 has significant therapeutic potential for tumor treatments. PD-L2 is a 25 kD type I transmembrane ligand of PD-1. Via PD-1, PD-L2 can serve as a co-inhibitor of T cell functions. Regulation of T cell responses, including enhanced T cell proliferation and cytokine production, can result from mAbs that block the PD-L2 and PD-1 interaction. Antigen Distribution PD-1 is expressed on a subset of CD4-CD8- thymocytes, and on activated T and B cells. Ligand/Receptor B7-H1 (PD-L1) and B7-DC (PD-L2) Function Lymphocyte clonal selection, peripheral tolerance NCBI Gene Bank ID UniProt.org Research Area Cancer . Immunology . Inhibitory Molecules References & Citations1.) Ardolino, M. et al. (2018) J Clin Invest. 128(10):4654-4668. PubMed 2.) Schreiber, RD. et al. (2017) Cancer Immunol Res. 5(2):106-117. 3.) Honjo, T. et al. (1992) EMBO J. 11:3887. 4.) Wurster S. et al. (2020) The Journal of Infectious Diseases 222(6):1989–994 Journal Link 5.) Lo, R. et al. (2021) Cancer Cell 39(10):1375-1387.e6 Journal Link Technical ProtocolsCertificate of Analysis |
Related Products
- -
- -
Prod No. | Description |
|---|---|
P362 | |
P377 | |
P383 | |
C2857 | |
P384 | |
P372 | |
P378 |
Formats Available
- -
- -
Prod No. | Description |
|---|---|
P377 | |
P383 | |
P384 | |
P501 | |
P378 |