Anti-Mouse CD279 (PD-1) (Clone RMP1-14) – Purified
Anti-Mouse CD279 (PD-1) (Clone RMP1-14) – Purified
Product No.: C2857
- -
- -
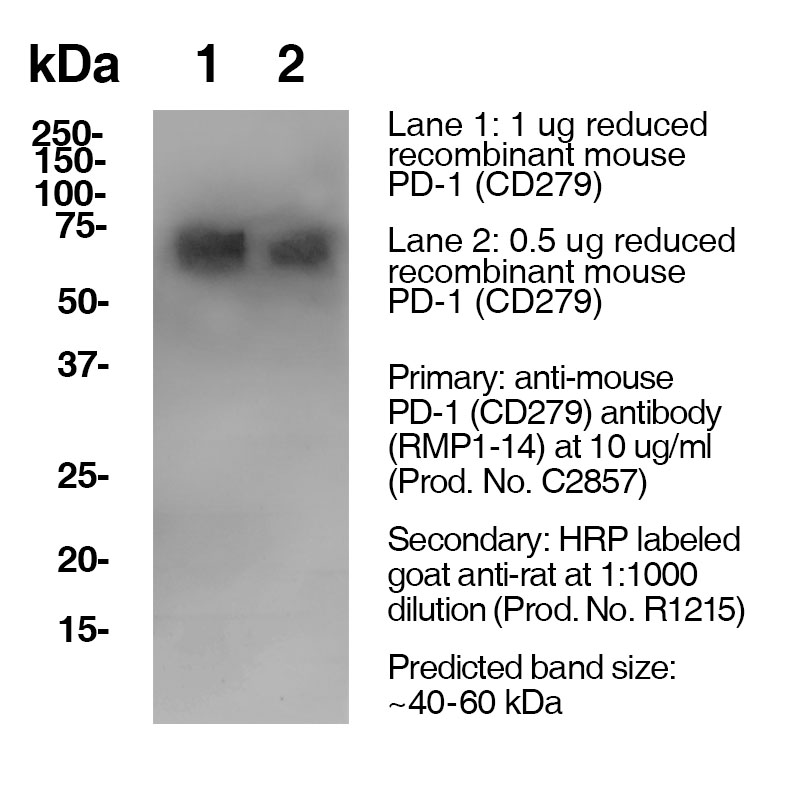
Clone RMP1-14 Target PD-1 Formats AvailableView All Product Type Monoclonal Antibody Alternate Names Programmed Death-1, CD279, PD1 Isotype Rat IgG2a κ Applications FC , IHC FFPE , WB |
Data
- -
- -
Antibody DetailsProduct DetailsReactive Species Mouse Host Species Rat Immunogen Subset of double negative thymocytes, activated T and B cells Product Concentration 0.5 mg/ml Formulation This purified antibody is formulated in 0.01 M phosphate buffered saline (150 mM NaCl) PBS pH 7.4, 1% BSA and 0.09% sodium azide as a preservative. Storage and Handling This purified antibody is stable when stored at 2-8°C. Do not freeze. Country of Origin USA Shipping Next Day 2-8°C RRIDAB_2829612 Each investigator should determine their own optimal working dilution for specific applications. See directions on lot specific datasheets, as information may periodically change. DescriptionDescriptionSpecificity Clone RMP1-14 recognizes an epitope on mouse PD-1. Background PD-1 is a 50-55 kD member of the B7 Ig superfamily. PD-1 is also a member of the extended CD28/CTLA-4 family of T cell regulators and is suspected to play a role in lymphocyte clonal selection and peripheral tolerance. The ligands of PD-1 are PD-L1 and PD-L2, and are also members of the B7 Ig superfamily. PD-1 and its ligands negatively regulate immune responses. PD-L1, or B7-Homolog 1, is a 40 kD type I transmembrane protein that has been reported to costimulate T cell growth and cytokine production. The interaction of PD-1 with its ligand PD-L1 is critical in the inhibition of T cell responses that include T cell proliferation and cytokine production. PD-L1 has increased expression in several cancers. Inhibition of the interaction between PD-1 and PD-L1 can serve as an immune checkpoint blockade by improving T-cell responses In vitro and mediating preclinical antitumor activity. Within the field of checkpoint inhibition, combination therapy using anti-PD1 in conjunction with anti-CTLA4 has significant therapeutic potential for tumor treatments. PD-L2 is a 25 kD type I transmembrane ligand of PD-1. Via PD-1, PD-L2 can serve as a co-inhibitor of T cell functions. Regulation of T cell responses, including enhanced T cell proliferation and cytokine production, can result from mAbs that block the PD-L2 and PD-1 interaction. Antigen Distribution PD-1 is expressed on a subset of CD4-CD8- thymocytes, and on activated T and B cells. Ligand/Receptor PD-L1 (B7-H1), PD-L2 Function Lymphocyte clonal selection, peripheral tolerance NCBI Gene Bank ID UniProt.org Research Area Apoptosis . Cancer . Cell Biology . Cell Death . Immunology . Inhibitory Molecules . Tumor Suppressors References & Citations1. Schreiber, RD. et al. (2017) Cancer Immunol Res. 5(2):106-117. 2. Honjo, T. et al. (1992) EMBO J. 11:3887. Technical ProtocolsCertificate of Analysis |
Related Products
- -
- -
Prod No. | Description |
|---|---|
P362 | |
P377 | |
P383 | |
C2857 | |
P384 | |
P372 | |
P378 |