Anti-Mouse Siglec-F – Purified (PhenoCycler-Fusion (CODEX)® Ready)
Anti-Mouse Siglec-F – Purified (PhenoCycler-Fusion (CODEX)® Ready)
Product No.: C2876
- -
- -
Clone E50-2440 Target Siglec-F Formats AvailableView All Product Type Monoclonal Antibody Isotype IgG2a κ Applications ELISA , FC , IF Microscopy , IHC , IHC FF , PhenoCycler® |
Data
- -
- -
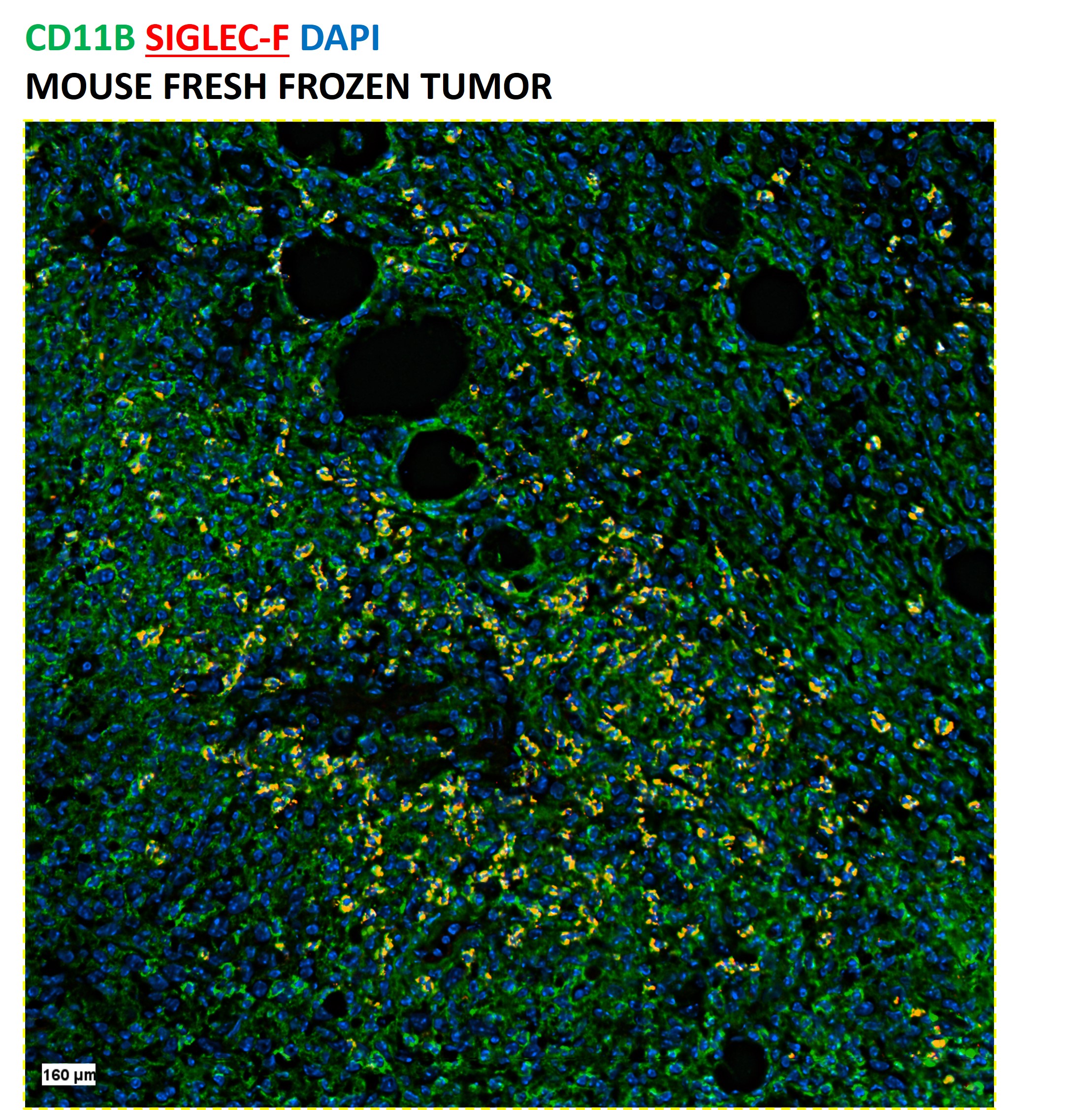
CODEX® DetailsValidation Notes Clone E50-2440 has been validated for use on CODEX® using human tonsil Fresh Frozen (FF) tissue. Tissue Screened Tonsil Tissue Preparation FF (Fresh Frozen) Antibody and Reporter DetailsReactivity Species Rat Host Species Mouse Concentration 0.5 mg/ml Formulation This purified antibody is formulated in 0.01 M phosphate buffered saline (150 mM NaCl) PBS pH 7.4. Storage and Handling The antibody solution should be stored undiluted at 4°C. Applications and Recommended Usage? Quality Tested by Leinco CODEX® This Siglec-F (Clone E50-2440) antibody is formulated to simplify the antibody preparation needed when performing a CODEX® barcode conjugate. The suggested concentration is 0.5 mg/ml.
ELISA4, FC3, 4, 5, IHC4, IF Microscopy4, B3, Country of Origin USA Each investigator should determine their own optimal working dilution for specific applications. See directions on lot specific datasheets, as information may periodically change. DescriptionSpecificity E50-2440 activity is directed against mouse Siglec-F. Antigen Distribution Siglec-F positive cells are expressed by eosinophils, alveolar macrophages, thymus and lung parenchyma tissues, and at very low levels on T cells. Siglec-F expression is restricted to cells of myelomonocytic lineage (CD11b-positive). Siglec-F is present on CD11blo (lo = low expressors) and CD11bhi (hi = low expressors) cell populations from mouse bone marrow, blood, and spleen but is especially high on the CD11blo cells. Cells that are CD11blo/Siglec-Fhi are predominantly immature cells of the myelomonocytic lineage, and cells that are CD11blo-hi/Siglec-Flo are mostly mature or immature neutrophils and monocytes, including leukocytes. Siglec-F is not expressed on mouse mast cells, stem cells, B cells, or NK cells. Background Siglecs (sialic acid-binding immunoglobulin superfamily lectins) are a family of single pass, transmembrane cell surface proteins characterized by shared structural motifs and an ability to recognize sialic acids1,2. Siglec-F selectively recognizes 6'-sulfo-sialyl Lewis X as a glycan ligand, and this interaction is inhibited by the E50-2440 antibody3. Siglec-F belongs to the Siglec-3 (CD33) group4 and is a functionally convergent paralog of human Siglec-83. Mouse Siglec-F is used as a model to understand glycan based therapeutic targeting strategies in humans1, 2.
Expression of Siglec-F on eosinophils3 plays a role in the allergic inflammatory response, during which its surface levels on eosinophils and other cells increase1. Siglec-F deficient mice that are exposed to allergen sensitization and asthma-inducing conditions display more pronounced bone marrow, blood, and tissue eosinophilia due to reduced apoptosis1 as well as exaggerated eosinophilic inflammation and tissue remodeling in asthma models2. Administration of Siglec-F antibody reduces blood and tissue eosinophils in vivo2. The rat monoclonal antibody E50-2440 was prepared by immunizing Lou rats with mSiglec-F-Fc, a fusion protein of the first two Ig-like domains of mouse Siglec-F and human IgG Fc fragment separated by an enterokinase cleavage site/FLAG tag (DYKDDDDK)4. Spleen cells were fused with Yb/20 myeloma cells, and hybridomas were screened by ELISA, tested by flow cytometry, and isotyped. The E50-2440 clone was selected based on its high staining intensity on primary cells. Siglec-F is a reliable marker of eosinophils among granulocytes in mouse1, and cellular staining profiles are identical in the C3H, Balb/c, and C57BL/6 mouse strains4. Antigen DetailsProtein PubMed References & Citations1. Bochner BS. Clin Exp Allergy. 39(3):317-324. 2009.
2. Kiwamoto T, Kawasaki N, Paulson JC, et al. Pharmacol Ther. 135(3):327-336. 2012. 3. Tateno H, Crocker PR, Paulson JC. Glycobiology. 15(11):1125-1135. 2005. 4. Angata T, Hingorani R, Varki NM, et al. J Biol Chem. 276(48):45128-45136. 2001. 5. Zhang JQ, Biedermann B, Nitschke L, et al. Eur J Immunol. 34(4):1175-1184. 2004. Technical Protocols |
Formats Available
- -
- -
Prod No. | Description |
|---|---|
C2876 | |
C2878 |
 Products are for research use only. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.
Products are for research use only. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.