Anti-Synaptotagmin-7 Antibody (56533)
Anti-Synaptotagmin-7 Antibody (56533)
Product No.: 56533
- -
- -
Clone S275-14 Target Synaptotagmin-7 Formats AvailableView All Product Type Monoclonal Alternate Names Synaptotagmin VII, SytVII Isotype Mouse IgG2b Applications IHC , WB , ICC/IF |
Data
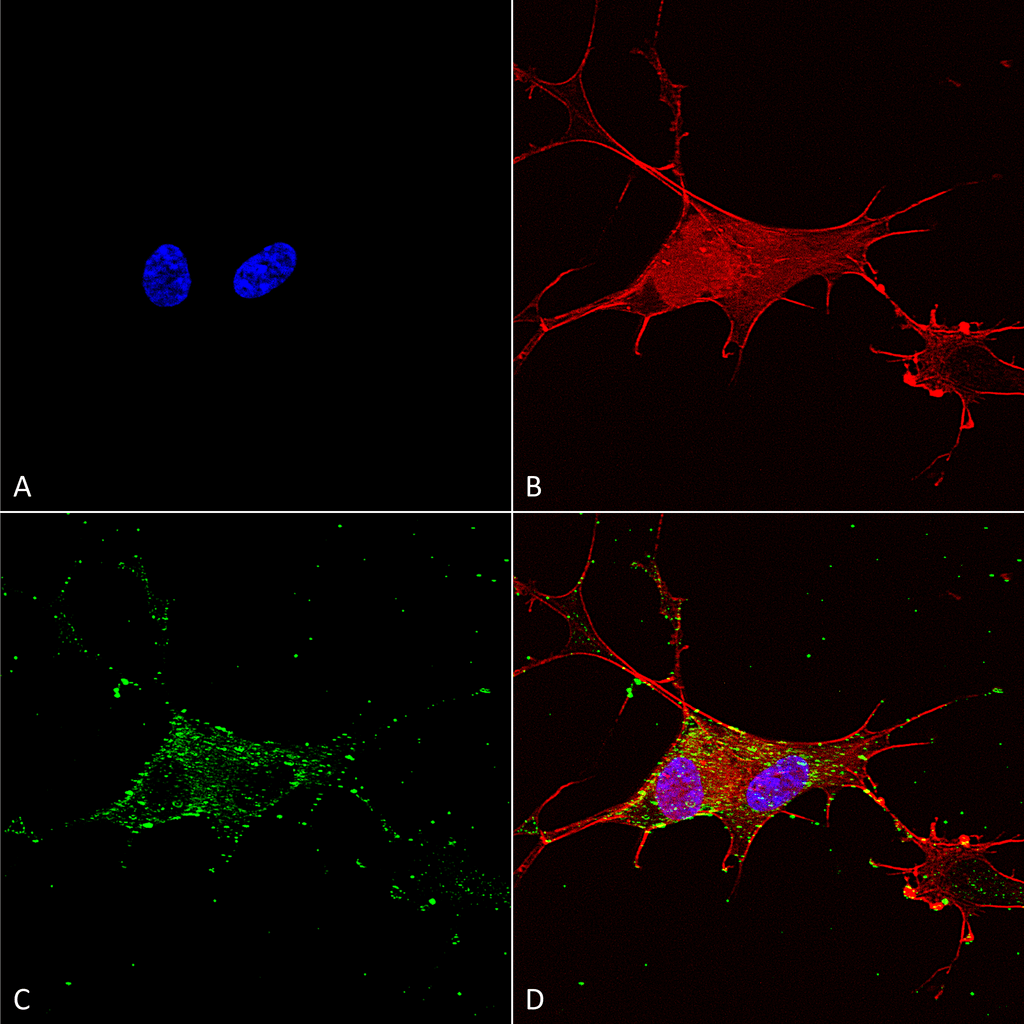 Immunocytochemistry/Immunofluorescence analysis using Mouse Anti-Synaptotagmin-7 Monoclonal Antibody, Clone S275-14 (56533). Tissue: Neuroblastoma cells (SH-SY5Y). Species: Human. Fixation: 4% PFA for 15 min. Primary Antibody: Mouse Anti-Synaptotagmin-7 Monoclonal Antibody (56533) at 1:100 for overnight at 4°C with slow rocking. Secondary Antibody: AlexaFluor 488 at 1:1000 for 1 hour at RT. Counterstain: Phalloidin-iFluor 647 (red) F-Actin stain; Hoechst (blue) nuclear stain at 1:800, 1.6mM for 20 min at RT. (A) Hoechst (blue) nuclear stain. (B) Phalloidin-iFluor 647 (red) F-Actin stain. (C) Synaptotagmin-7 Antibody (D) Composite.
Immunocytochemistry/Immunofluorescence analysis using Mouse Anti-Synaptotagmin-7 Monoclonal Antibody, Clone S275-14 (56533). Tissue: Neuroblastoma cells (SH-SY5Y). Species: Human. Fixation: 4% PFA for 15 min. Primary Antibody: Mouse Anti-Synaptotagmin-7 Monoclonal Antibody (56533) at 1:100 for overnight at 4°C with slow rocking. Secondary Antibody: AlexaFluor 488 at 1:1000 for 1 hour at RT. Counterstain: Phalloidin-iFluor 647 (red) F-Actin stain; Hoechst (blue) nuclear stain at 1:800, 1.6mM for 20 min at RT. (A) Hoechst (blue) nuclear stain. (B) Phalloidin-iFluor 647 (red) F-Actin stain. (C) Synaptotagmin-7 Antibody (D) Composite.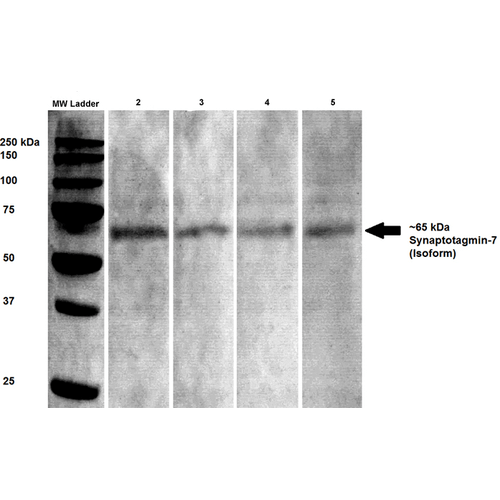 Western Blot analysis of Rat brain lysates showing detection of Synaptotagmin 7 protein using Mouse Anti-Synaptotagmin 7 Monoclonal Antibody, Clone S275-14 (56533). Primary Antibody: Mouse Anti-Synaptotagmin 7 Monoclonal Antibody (56533) at 1:100, 1:250, 1:500, and 1:1000.
Western Blot analysis of Rat brain lysates showing detection of Synaptotagmin 7 protein using Mouse Anti-Synaptotagmin 7 Monoclonal Antibody, Clone S275-14 (56533). Primary Antibody: Mouse Anti-Synaptotagmin 7 Monoclonal Antibody (56533) at 1:100, 1:250, 1:500, and 1:1000.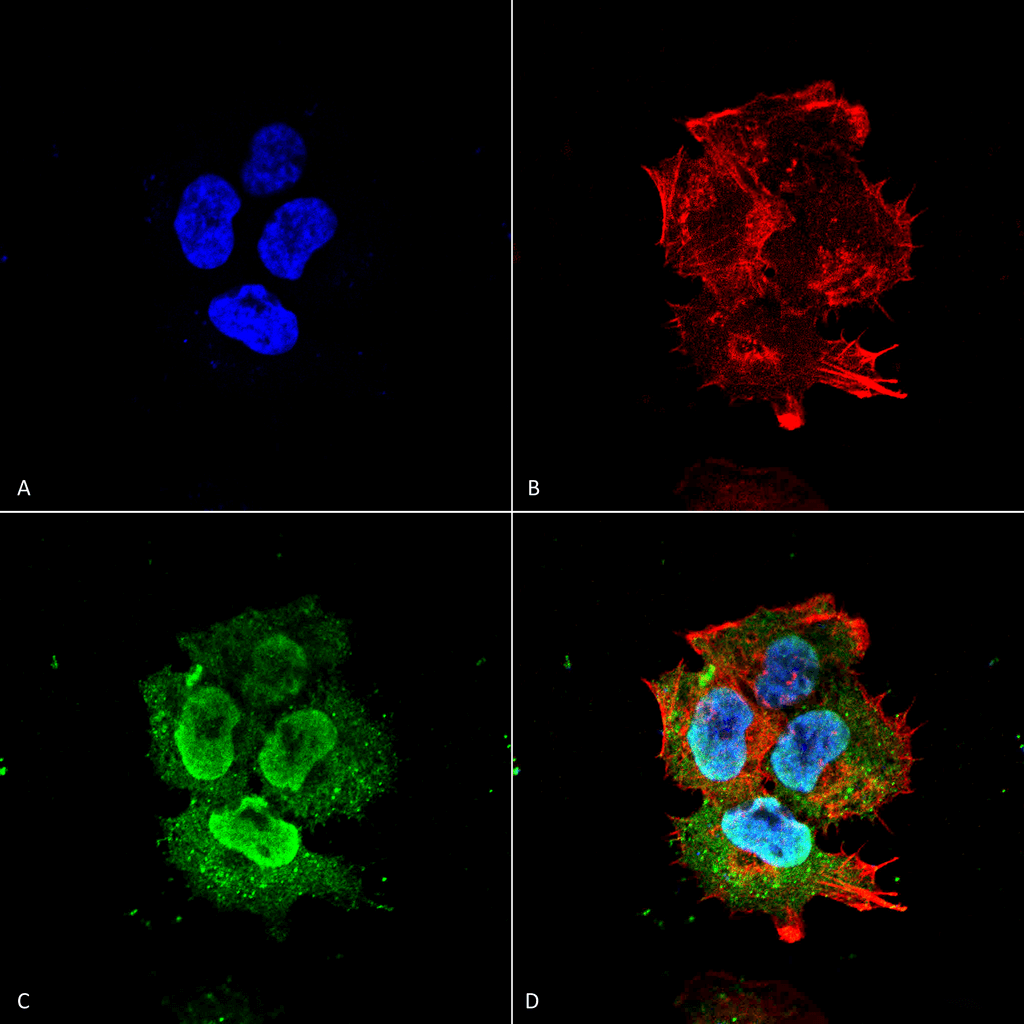 Immunocytochemistry/Immunofluorescence analysis using Mouse Anti-Synaptotagmin-7 Monoclonal Antibody, Clone S275-14 (56533). Tissue: Neuroblastoma cell line (SK-N-BE). Species: Human. Fixation: 4% Formaldehyde for 15 min at RT. Primary Antibody: Mouse Anti-Synaptotagmin-7 Monoclonal Antibody (56533) at 1:100 for 60 min at RT. Secondary Antibody: Goat Anti-Mouse ATTO 488 at 1:100 for 60 min at RT. Counterstain: Phalloidin Texas Red F-Actin stain; DAPI (blue) nuclear stain at 1:1000; 1:5000 for 60 min RT, 5 min RT. Localization: Cytoplasmic Vesicle, Nucleus. Magnification: 60X. (A) DAPI (blue) nuclear stain. (B) Phalloidin Texas Red F-Actin stain. (C) Synaptotagmin-7 Antibody. (D) Composite.
Immunocytochemistry/Immunofluorescence analysis using Mouse Anti-Synaptotagmin-7 Monoclonal Antibody, Clone S275-14 (56533). Tissue: Neuroblastoma cell line (SK-N-BE). Species: Human. Fixation: 4% Formaldehyde for 15 min at RT. Primary Antibody: Mouse Anti-Synaptotagmin-7 Monoclonal Antibody (56533) at 1:100 for 60 min at RT. Secondary Antibody: Goat Anti-Mouse ATTO 488 at 1:100 for 60 min at RT. Counterstain: Phalloidin Texas Red F-Actin stain; DAPI (blue) nuclear stain at 1:1000; 1:5000 for 60 min RT, 5 min RT. Localization: Cytoplasmic Vesicle, Nucleus. Magnification: 60X. (A) DAPI (blue) nuclear stain. (B) Phalloidin Texas Red F-Actin stain. (C) Synaptotagmin-7 Antibody. (D) Composite. - -
- -
Antibody DetailsProduct DetailsReactive Species Mouse ⋅ Rat Host Species Mouse Immunogen Fusion protein corresponding to aa 150-239 of mouse Synapto- tagmin-7 (accession no.Q9R0N7). Product Concentration 1.0 mg/ml Formulation PBS, pH 7.4, 50% glycerol, 0.09% sodium azide.Purified by Protein G affinity chromatography. State of Matter Liquid Product Preparation Purified by Protein G affinity chromatography Storage and Handling This antibody is stable for at least one (1) year at -20°C. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
Regulatory Status For in vitro investigational use only. Not
intended for diagnostic or therapeutic
applications. Country of Origin USA Shipping Next Day 2-8°C Applications and Recommended Usage? Quality Tested by Leinco Immunoblotting: use at 1ug/mL. Predicted molecular weight is ~45kDa. Other isoforms of ~65kDa are also detected.
Positive control: rat brain lysate. These are recommended concentrations. Endusers should determine optimal concentrations for their applications. Each investigator should determine their own optimal working dilution for specific applications. See directions on lot specific datasheets, as information may periodically change. DescriptionDescriptionSpecificity This antibody recognizes mouse and rat
Synaptotagmin-7. It does not cross-react with other Synaptotagmins. Background Synaptotagmins constitute a family of membrane trafficking proteins that are characterized by an N terminal trans- membrane region (TMR), a variable linker,and two C-terminal C2 domains: C2A and C2B. There are 15 members in the mammalian synaptotagmin family. The synaptotagmins are integral membrane proteins of synaptic vesicles thought to act as Ca+2 sensors in vesicular trafficking and exocytosis. Calcium binding to synaptotagmin triggers neurotransmitter release at the synapse. The first C2 domain mediates Ca+2-dependent phospholipid binding. The second C2 domain mediates interaction with Stonin 2. Function Ca(2+) sensor involved in Ca(2+)-dependent exocytosis of secretory and synaptic vesicles through Ca(2+) and phospholipid binding to the C2 domain. Ca(2+) induces binding of the C2-domains to phospholipid membranes and to assembled SNARE-complexes; both actions contribute to triggering exocytosis. SYT7 binds Ca(2+) with high affinity and slow kinetics compared to other synaptotagmins (PubMed:26738595). Involved in Ca(2+)-triggered lysosomal exocytosis, a major component of the plasma membrane repair (By similarity). Ca(2+)-regulated delivery of lysosomal membranes to the cell surface is also involved in the phagocytic uptake of particles by macrophages (PubMed:16982801, PubMed:21041449). Ca(2+)-triggered lysosomal exocytosis also plays a role in bone remodeling by regulating secretory pathways in osteoclasts and osteoblasts (PubMed:18539119). Involved in cholesterol transport from lysosome to peroxisome by promoting membrane contacts between lysosomes and peroxisomes: probably acts by promoting vesicle fusion by binding phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate on peroxisomal membranes (PubMed:25860611). Acts as a key mediator of synaptic facilitation, a process also named short-term synaptic potentiation: synaptic facilitation takes place at synapses with a low initial release probability and is caused by influx of Ca(2+) into the axon terminal after spike generation, increasing the release probability of neurotransmitters (PubMed:24569478, PubMed:26738595). Probably mediates synaptic facilitation by directly increasing the probability of release (PubMed:26738595). May also contribute to synaptic facilitation by regulating synaptic vesicle replenishment, a process required to ensure that synaptic vesicles are ready for the arrival of the next action potential: SYT7 is required for synaptic vesicle replenishment by acting as a sensor for Ca(2+) and by forming a complex with calmodulin (PubMed:24569478). Also acts as a regulator of Ca(2+)-dependent insulin and glucagon secretion in beta-cells (PubMed:18308938, PubMed:19171650). Triggers exocytosis by promoting fusion pore opening and fusion pore expansion in chromaffin cells (PubMed:20956309). Also regulates the secretion of some non-synaptic secretory granules of specialized cells (By similarity). {UniProtKB:Q62747, PubMed:16982801, PubMed:18308938, PubMed:18539119, PubMed:19171650, PubMed:20956309, PubMed:21041449, PubMed:24569478, PubMed:25860611, PubMed:26738595}. NCBI Gene Bank ID UniProt.org Research Area Neuroscience References & CitationsTechnical ProtocolsCertificate of Analysis |
Formats Available
 Products are for research use only. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.
Products are for research use only. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.


