Anti-Ubiquitin [Clone 5B9.B3]
Anti-Ubiquitin [Clone 5B9.B3]
Product No.: 11023
- -
- -
Clone 5B9.B3 Target Ubiquitin Formats AvailableView All Product Type Monoclonal Isotype Mouse IgG2a Applications ELISA , WB |
Data
- -
- -
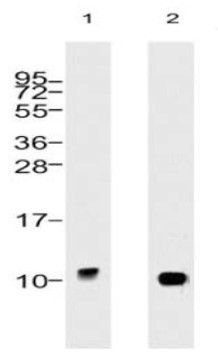
Antibody DetailsProduct DetailsReactive Species Bovine ⋅ Human ⋅ Mouse ⋅ Rat Host Species Mouse Immunogen Native bovine ubiquitin conjugated to KLH Product Concentration Lot Specific Formulation PBS, pH 7.4. State of Matter Liquid Product Preparation Purified by Protein G affinity chromatography Storage and Handling This antibody is stable for at least one (1) year at -20°C. Avoid repeated freezing and thawing. Regulatory Status Research Use Only Country of Origin USA Shipping Next Day 2-8°C Applications and Recommended Usage? Quality Tested by Leinco Immunoblotting: use at 1ug/mL.
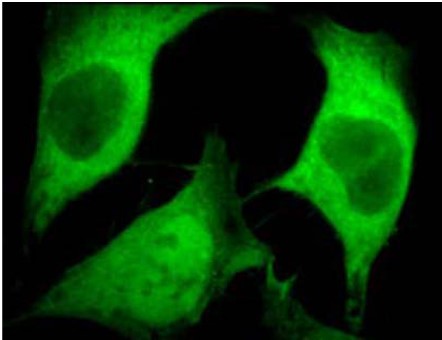
Immunofluorescence: use at 10ug/mL. A band of ~10kDa is detected ELISA: use at 1ug/mL with ubiquitin on the solid phase. These are recommended concentrations. Enduser should determine optimal concentrations for their applications. Each investigator should determine their own optimal working dilution for specific applications. See directions on lot specific datasheets, as information may periodically change. DescriptionDescriptionSpecificity This antibody recognizes human, mouse, rat, and bovine ubiquitin. Other species have not been investigated. Background Ubiquitin, a small protein comprised of 76 amino acids with a molecular mass of approximately 10kDa, is highly conserved among eukaryotic species. The primary role of ubiquitin is to clear abnormal, foreign, and improperly folded proteins by targeting them for degradation by the 26S proteosome. Ubiquitination of proteins is an essential process that is regulated by ubiquitin- activating enzymes, ubiquitin-conjugating enzymes, and ubiquitin-protein ligases. Ubiquitination also occurs in the internalization and degradation of plasma membrane proteins. Function [Ubiquitin]: Exists either covalently attached to another protein, or free (unanchored) (By similarity). When covalently bound, it is conjugated to target proteins via an isopeptide bond either as a monomer (monoubiquitin), a polymer linked via different Lys residues of the ubiquitin (polyubiquitin chains) or a linear polymer linked via the initiator Met of the ubiquitin (linear polyubiquitin chains) (PubMed:26116755). Polyubiquitin chains, when attached to a target protein, have different functions depending on the Lys residue of the ubiquitin that is linked: Lys-6-linked may be involved in DNA repair; Lys-11-linked is involved in ERAD (endoplasmic reticulum-associated degradation) and in cell-cycle regulation; Lys-29-linked is involved in proteotoxic stress response and cell cycle; Lys-33-linked is involved in kinase modification; Lys-48-linked is involved in protein degradation via the proteasome; Lys-63-linked is involved in endocytosis, DNA-damage responses as well as in signaling processes leading to activation of the transcription factor NF-kappa-B (By similarity). Linear polymer chains formed via attachment by the initiator Met lead to cell signaling (By similarity). Ubiquitin is usually conjugated to Lys residues of target proteins, however, in rare cases, conjugation to Cys or Ser residues has been observed (By similarity). When polyubiquitin is free (unanchored-polyubiquitin), it also has distinct roles, such as in activation of protein kinases, and in signaling (By similarity). {UniProtKB:P0CG47, PubMed:26116755}. NCBI Gene Bank ID UniProt.org Research Area Apoptosis References & CitationsTechnical ProtocolsCertificate of Analysis |